Hands-on Guide on How to Attack Networks with Wifite
Hands-on Guide on How to Attack Networks with "Wifite"
Introduction
Hi readers, this guide will be an overview of a powerful tool called "Wifite".
In this article we are going to cover:
- Introduction to networking
- Wireless Networks Attacks and Wifite Overview
- WEP
- WPA/WPA2
- WPS
Introduction to Networking
Before diving deep into how to use Wifite I believe that we need to explore some networking fundamentals first. It is essential to learn how a network works. Networking is the process of changing information between different devices. The transmission is usually done using a transmission mode. In communications we have generally 3 transmission modes:
- Simple Mode : in this mode, the data is transferred in one direction like the transmission used in TV broadcasting
- Half-duplex Mode : in this mode, the data flows in two directions but using a single mean of communication
- Full-duplex Mode : in this mode, the data flow is bidirectional and simultaneous.
When it comes to communication networks we have many types. Some of them are the following:
- Local Area Network (LAN): this network is used in small surfaces and areas
- Metropolitan area network (MAN): this network is larger than the Local Area Network. We can use it for example to connect two offices.
- Wide area network (WAN): We use this type of networks to connect large distances
- Personal area network (PAN): this network is used in short distances and small areas like a single room.
By Definition: "The Open Systems Interconnection model (OSI model) is a conceptual model that characterizes and standardizes the communication functions of a telecommunication or computing system without regard to its underlying internal structure and technology. Its goal is the interoperability of diverse communication systems with standard protocols. The model partitions a communication system into abstraction layers. The original version of the model defines seven layers.
A layer serves the layer above it and is served by the layer below it. For example, a layer that provides error-free communications across a network provides the path needed by applications above it, while it calls the next lower layer to send and receive packets that comprise the contents of that path. Two instances at the same layer are visualized as connected by a _horizontal _connection in that layer.
The model is a product of the Open Systems Interconnection project at the International Organization for Standardization(ISO), maintained by the identification ISO/IEC 7498-1." (Source: Wikipedia)
In other words, data is moving in the network respecting a specific order. The following are the seven Layers of the OSI Model:
7- Application layer
6 -Presentation layer
5- Session layer
4- Transport layer
3- Network layer
2- Data link layer
1- Physical layer
Wireless Networks
According to Techopedia:
"Wireless networks are computer networks that are not connected by cables of any kind. The use of a wireless network enables enterprises to avoid the costly process of introducing cables into buildings or as a connection between different equipment locations."
Wireless Network Attacks and Wifite overview:
We all know that there are many network attacks in the wild that black hat hackers can use in order to attack an organization. In this section, we are going to focus on only a few wireless attacks since we are going to explore a wireless attack tool which is "Wifite". Their developers describe it as follows:

Wifite is designed to use all known methods for retrieving the password of a wireless access point (router). These methods include:
- WPS__: The Offline Pixie-Dust attack
- WPS: The Online Brute-Force PIN attack
- WPA : The WPA Handshake__ Capture + offline crack.
- WPA: The PMKID Hash Capture + offline crack.
- WEP__: Various known attacks against WEP, including fragmentation, chop-chop, aireplay, etc.
Run wifite, select your targets , and Wifite will automatically start trying to capture or crack the password.
If you are using Kali Linux you will already find it there. Kali Linux is a Debian-derived Linux distribution designed for digital forensics and penetration testing. It was developed and maintained by offensive security ( https://www.offensive-security.com )
To learn how to install it, I highly recommend you to read my article:
Or you can download it from here: https://github.com/derv82/wifite2
git clone https://github.com/derv82/wifite2.git cd wifite2 sudo ./Wifite.py
Wifite was developed by Derv Merkler under GPLv2 license. The tool:
- sorts targets by signal strength (in dB); cracks closest access points first
- automatically de-authenticates clients of hidden networks to reveal SSIDs
- smart__ WPA de-authentication; cycles between all clients and broadcast deauths
- all passwords saved to cracked.txt (Source: https://tools.kali.org/wireless-attacks/wifite )
Wifite requires the Aircrack-ng suite (airmon-ng,airodump-ng,aireplay-ng,packetforge-ng, and aircrack-ng)
Let's explore the tool:
Go to your Kali machine and type
Wifite -h
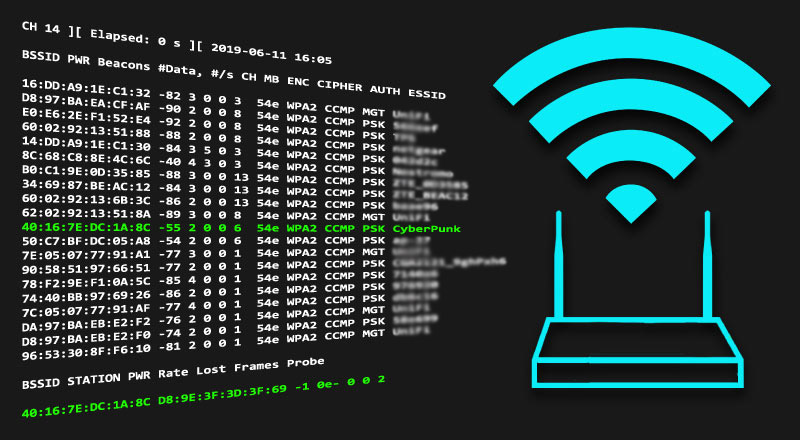
To start scanning the area for access point type:
wifite --showb
It will provide pieces of information about your targets.
Wifite gives you the ability to change your MAC address when performing the operations. You need to simply provide the "-mac" option
Wifite -mac \<Other Options>
WEP protected routers
Wifite gives you the ability, as previously discussed to attack WEP and WPA/WPA2
Wired Equivalent Privacy is a security algorithm for IEEE 802.11 wireless networks. Introduced as part of the original 802.11 standard ratified in 1997, its intention was to provide data confidentiality comparable to that of a traditional wired__ network. (Wikipedia)
Let's say that you decided to crack a WEP password. Pass the following options:
--wep
--require-fakeauth
--keep-ivs
Don't forget to select network NUM (you can give numbers separated by a comma or select all )
WPA/WPA2 protected routers
Wi-Fi Protected Access, Wi-Fi Protected Access II, and Wi-Fi Protected Access 3 are three security protocols and security certification programs developed by the Wi-Fi Alliance to secure__ wireless computer networks.(Wikipedia)
To crack WPA/WPA2 you can use the following options
--WPA
Capture new handshakes
--new-hs
Provide a dictionary/wordlist
--dict \<file>
Usually, you can find some helpful wordlists in Kali Linux in this repository:
/usr/share/wordlists
You can select one of them or create a new one
WPS
WPS stands for Wi-Fi Protected Setup. It is a wireless network security standard that tries to make connections between a router and wireless devices faster and easier. (Wikipedia)
Evil Twin
To perform Evil Twin attack against all the targets, use:
-ev
or
--eviltwin
Sniffing attacks
Sniffing is the process of intercepting network traffic by turning the network interface card (NIC) to promiscuous mode, in order to be able to sniff the transmitted data. There are two types of network sniffing – active and passive sniffing:
- Passive sniffing: This occurs at hub devices or switches without injecting any additional packets.
- Active sniffing: This is done by injecting Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) packets into the network. The following are some active network sniffing attacks:
- MAC flooding —this is the process of flooding the CAM table with random data until it is full
- Switch port stealing
These two previous attacks could be avoided by allowing only one MAC address on the switch port and implementing port security.
ARP Poisoning: ARP is used to resolve MAC addresses. An attacker could forge the ARP requests to flood a switch. It is called poisoning when they flood the ARP cache.
MAC spoofing : This is the act of sniffing a MAC address and using it in another context. To defend against this attack, you need to block traffic that is not mentioned in the binded table.
Summary
In this article, we explored some networking fundamentals. Later we discovered a powerful tool called Wifite and how to use it in order to attack networks.